|
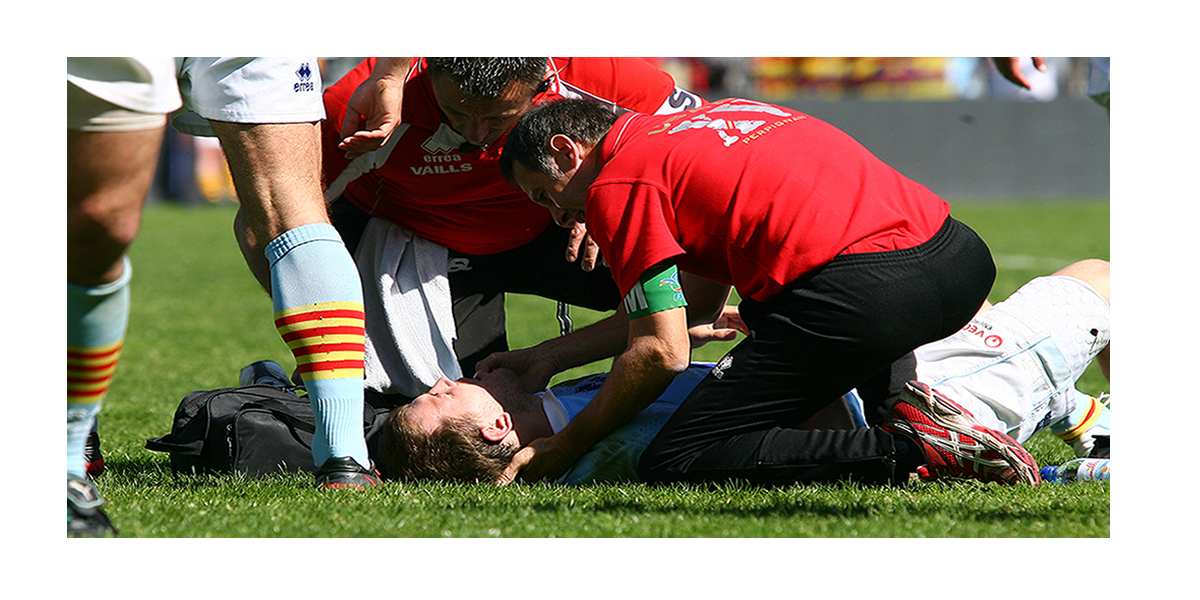
Not all brain injuries lead to changes in perception or thought processes, but those that do can be a source of great frustration for the sufferer. Brain injuries can affect one’s capacity to learn, work, or interact with others.
Lack of Insight
Because people with brain injury often find it difficult to recognize or accept that their cognition has changed, it’s important to explain patiently, clearly, and as often as necessary why they’re being treated or why they can no longer perform certain tasks. This can be extremely frustrating for the sufferer, who may not believe or listen to you. If this occurs, try talking about something else. Reasoning may not be possible and arguing will only upset you both. In time, the person will learn to adapt. Memory Problems
These are very common. Long-term memory may remain completely unaffected, while short-term memory and/or the ability to form new memories may suffer significantly. These problems may disappear over time, but if they don’t, seeking ways to compensate for the deficit may be more successful than trying techniques like repetition. Concentration Problems
Victims of brain injury are often easily distracted and unable to concentrate, and they may have trouble following a conversation. Sluggish Response Times
A person with a brain injury may take a long time to reply to questions or complete tasks. Patience here is key, as is keeping sufferers away from situations where a sluggish response may be harmful (e.g. driving). Planning and Problem-solving Issues
Organization and planning may be difficult for people with a brain injury. Breaking down complex tasks into smaller, simpler steps will help them to accomplish things and stay organized. Lack of Initiative
Some people with a brain injury are unable to motivate themselves. They may need to be prompted to dress, shower, or reply to a question. Inflexibility
Brain injury victims often have trouble switching mental gears, so they may repeat themselves or struggle to sympathize with the perspectives of others. Changes in routine may throw or upset them. Depression
This is quite common and generally occurs some time after the injury. It may lead to listlessness, insomnia or hypersomnia, sadness, weight loss and decreased sexual activity. © 2008 BIC |
What is Brain Injury?
Brain injury can be a devastating disability, and given the brain’s complexity and the differences in the types, locations, and extent of damage, the effects of a brain injury can be wide and varied. Some occur immediately, and some may take days or even years to appear.
© Brain Injury Center 2015
Contact Us
The Human Brain
The human brain in an incredible thing! It’s one of the most complex and least understood parts of the human body, but science is making new advances every day that tell us more about the brain.
The average human brain is 5.5 inches wide and 3.6 inches high. When we’re born, our brains weigh about 2 pounds, while the adult brain weighs about 3 pounds.
The brain accounts for about 2% of your total body weight, but it uses 20% of your body’s energy!
It sends out more electrical impulses in one day than all the telephones in the world, and it’s estimated that the brain thinks about 70,000 thoughts in a 24-hour period.
Warning: Graphic photo
© 2008-2015 Brain Injury Centre